Contact vision correction is the correction of defects with the help of lenses. The use of lenses, materials for their manufacture. Indications for contact correction
In 1962, George Essen created corrective lenses, calling them orthofocus. A few years later, Newton Wesley suggested that the science of them be called orthokeratology. Unfortunately, the first orthokeratology lenses were unpredictable and unstable, and the effect of their use was weak. They were made of airtight materials, which is why they were only allowed to be worn during the day. Since then, orthokeratology has come a long way, and today we have a large selection of high quality corrective night lenses.
Will he wear them all the time?
The quality of their material allows the younger to wear them for extended wear and limit manipulation. But in special occasions your ophthalmologist will have to choose equipment for soft lenses. Adaptation provides the possibility of long wear. He wears them for baths and showers. Lenses should be removed and cleaned once a week on average. These manipulations will be learned during adaptation. If your child loses a lens while rubbing their eyes, they should rest after cleaning.
The wearing of lenses should not exclude the child from any activities carried out at school. Your ophthalmologist will explain the instructions to be given to the teaching team. The child does not have to wear contact lenses to go to the pool. Losses are the most common complications at this age. They appear to be rarer in hard lenses than soft lenses and decrease as the child gets used to the lenses.
How lenses work
Let's figure out how night lenses work. They squeeze the cornea, thereby correcting its shape. At the same time, only the thickness of the epithelium, the superficial thin layer of the cornea, changes in a person. The stroma and endothelium remain unchanged.
A person puts on hard lenses at night and goes to bed peacefully. While he is resting, the devices do their work. They gently press on the cornea, correcting irregularities, correcting thickness, shape and curves. After waking up, a person removes medical night lenses and goes about his business. He has good eyesight throughout the day.
Are controls frequent?
Infections are virtually non-existent in hard lenses, but are more common, though rare, in soft lenses. In the case of nasopharyngeal infections, the child should not sleep with their lenses. Yes, a child's vision changes rapidly and your ophthalmologist will check vision, lens shape and condition three to four times a year. Lenses will be updated once or twice a year. According to these medical indications, social Security partially supports one lens per eye per year, and the add-on is responsible for your additional reimbursement arrangements in accordance with the contract you signed.
Validity
Previously, doctors were sure that orthokeratological hard lenses have only a temporary effect, and after their removal, the cornea soon returns to its former shape. However, recent Scientific research proved otherwise. As it turned out, with many months of use, hard lenses can cause a lasting effect. In children who wore them for about 4 years, minor corneal changes persisted for more than two weeks.
A teenager often seeks better self-esteem and refuses his glasses. Failure to listen to this aesthetic demand may lead a teenager to refuse to wear the glasses necessary to complete his visual development. The adaptation of the lens gives rise to a certain psychological flowering during this period of conflict.
Can a teenager wear contact lenses?
Yes, if he expresses a desire, because it is a visual, sports or aesthetic motivation. The ophthalmologist, having studied the visual defect in the shape of the eye, will advise the type of lens adapted to his needs. But adjusting as a teenager means adapting over many years. In addition, he will wear lenses every day and for a long time during the day, because when he gets rid of glasses, he does not want to wear them. Your ophthalmologist will select the safest equipment based on its correction and performance.
Modern night lenses for the eyes can correct vision for a period of one to three days. The duration of their action depends on the degree of myopia and individual characteristics human eye. Immediately after removing the lenses, visual acuity rises to 100%, but in the evening it drops by 0.5-0.75 diopters.
Peculiarities
When it comes to choosing a remedy, people are lost and unable to make a decision. Therefore, we will compare night lenses for restoring vision with daytime ones. This will help you evaluate their advantages and disadvantages, as well as understand which ones to choose.
Rigid lenses for major corrections or astigmatisms; Daily renewal of soft lenses; Orthokeratology lenses for some myopia. A teenager should only handle and care for their own lenses. He must understand the interest of the interview and respect its conditions. Otherwise, you must know to stop wearing lenses. The "lens contract" is concluded between an ophthalmologist and a teenager. However, parents should ensure good practice and be vigilant.
What defects can be corrected in contact lenses?
Check-ups by an ophthalmologist should be regular once or twice a year. All visual anomalies of a teenager can be corrected in contact lenses max, provided that the lenses produce a visual quality at least equal to that obtained with spectacles. Lincellar equipment in case of accommodative strabismus avoids stress on the eye, which squints from taking off the glasses.
| Hard nights | Soft day | |
| Application possibilities | Correct myopia less than - 6.5 D and myopic astigmatism up to - 1.75 D. They are rarely used to combat hyperopia, but they are able to correct hypermetropia less than + 3.0 D. |
They can correct myopia and almost any degree. Only toric and rigid daily lenses are suitable for astigmatism correction. |
| Speed of action | One hundred percent recovery of vision occurs only after a few days or weeks. | Vision improves immediately after putting on the lens. |
| Replacement frequency | The shelf life of a pair of lenses is 1 year. The appearance of small scratches does not prevent their further use. | They can be worn for 1, 3, 6 months or a year. If scratches appear, they must be replaced immediately. |
| Advantages and disadvantages | They allow you to engage in extreme sports, work in smoky rooms, cry, visit beaches, baths, and pools without fear. | They should be removed before going to bed and instillation. eye drops. When working in an air-conditioned room, they cause the development of dry eye syndrome. |
Indications and contraindications
Night contact lenses are indicated for people with myopia and myopic astigmatism. They should be chosen by men and women who do not want to do laser correction vision. Medical lenses save people whose professions do not allow the wearing of glasses or any other means of correction. They can be used by athletes, the military, workers of chemical plants and people who are forced to stay in dusty rooms for a long time.
Are there contraindications?
Some common drugs, especially anticancer drugs, are contraindicated for wearing soft lenses due to the dryness of the eye caused. Taking pills does not oppose lens wear, but may change the parameters of the eye, make lenses uncomfortable, and require rehabilitation.
Do lenses return?
Swimming in the pool is prohibited due to the risk of infection, and the teenager must remove the lenses to swim or replace them with disposable daily lenses, which he will throw away immediately after swimming. Yes, in some cases it is provided with boxes, depending on the visual defect. Not in most cases, your refund additional organization depending on the contract you signed.
Night lenses to improve vision are suitable for children and adolescents with progressive myopia. Scientists conducted a series of studies and concluded that contact correction slows down the development of myopia by more than two times.
Contraindications to the use of corrective night lenses:
- corneal deformities in the form of keratoconus or keratoglobus;
- severe dry eye syndrome;
- astigmatism over 1.75 and myopia over 6.5 diopters;
- , lagophthalmos;
- , blepharitis, keratitis and others inflammatory diseases eye.
Application in childhood
Orthokeratology is beneficial for children and adolescents with myopia as it helps them maintain their vision. The use of hard night contact lenses is The best way stop the rapid development of myopia. Their use helps to relieve visual fatigue and tension, temporarily restore vision and even improve it.
This is a revolution that could please the 30 million French people who wear glasses. Although advances in surgery or ophthalmic techniques have increased significantly, the number of French people with visual problems is becoming increasingly important. But this observation may well change.
Night lenses for myopia correction
Say goodbye to glasses and daily lenses. In addition to surgery, a new invention could help shortsighted people get rid of their correction during the day with night lenses: orthokeratology, which is much less than the cost of surgery and is equivalent to conventional lenses.
Night lenses can be used in children over 6 years of age. Only an experienced ophthalmologist should select them. Before prescribing a corrective agent, the specialist must carefully examine the child and make sure that he does not have accommodation spasm (the so-called false myopia). Unlike true myopia, this disease is treated with eye drops. Wearing lenses in this case is prohibited. With adequate treatment of false myopia, the baby's vision will soon improve.
Wear lenses for at least six o'clock in the evening for clear vision the next day. Wearing these lenses changes the curve of the cornea which influences the view of each one. If it seems effective for myopia and even astigmatism, it starts slowly for farsightedness. We feel that doctors are becoming more and more interested. We felt the cultural drag on wearing lenses at night, but this is changing with all the research that proves its benefits, Menicon Laboratories, who specialize in translucent rigid lenses, responded.
Selection rules
Night lenses - which one is better? Orthokeratology rigid night lenses can be purchased from a contact lab or optometrist. Only an ophthalmologist who has completed special training courses and has all the necessary skills can pick them up. You cannot make a choice on your own.
A person who previously wore soft contact lenses should stop wearing them for 2 weeks. Only after that he can go for a consultation with a specialist.
eye enlargement app
But the nearsighted 40% aren't the only ones who can hope to get rid of their fix, presbyopes too. The application offers many exercises for this to be performed three times a week for early stages before performing a session of 15 minutes per week two months later.
Restrictions due to visual defects are often an obstacle to normal activities. The use of corrective tools such as glasses or contact lenses can be a hindrance both at work and during school or leisure time.
The selection of lenses begins with an examination, which includes:
- determination of visual acuity;
- refractometry;
- keratotopography;
- keratometry;
- other necessary studies.
The choice of orthokeratology lenses is quite complicated, which is why the specialist has to reconsider several options. As a result, the doctor chooses a correction tool that is best suited in all respects. A person puts on lenses and sleeps in them for 6-7 hours, then comes back for a second examination. If they fit, the doctor allows you to use them all the time.
Orthokeratology lenses correct your visual defect while you sleep, allowing you to see clearly with the naked eye without the need for glasses or contact lenses. Unlike regular contact lenses, orthokeratology lenses are not worn during the day, but are worn at bedtime and removed in the morning. This allows you to see well with the naked eye, without contact lenses and without glasses for the rest of the day. By placing your lenses every night, you will see well all day. If you decide to stop using lenses, your eye will soon return to its original state thanks to the reversibility of orthokeratology.
Paragon night lenses are the most popular in our time. They can be purchased at many opticians and even ordered online. Note that when buying them, a person receives free consultation ophthalmologist.

Some applicators have developed orthochonathological procedures associated with the use of night lenses: the cornea is formed during sleep, and the lenses are removed upon awakening, and in most cases the effect lasts until the evening. This method has the advantage of limiting the discomfort of the hard lens caused by eyelid blinking and eliminating the components environment, which can cause lens intolerance during the day; in addition, the rate of corneal remodeling increases under the pressure created by closed eyelids.
For nighttime use, materials with very high oxygen permeability must be used to ensure sufficient oxygenation of the cornea even when the eyelids are closed. In this sense, modern orthokeratology has taken advantage of the presence of rigid, permeable gaseous materials. Today, there are hyperpermeable oxygen materials that are significantly more compatible with corneal physiology and greatly enhance the efficacy and safety of orthokeratology as well as conventional contact theory.
Side effects when using
At first, wearing orthokeratology lenses can lead to side effects. Patients often have a feeling of dryness in the eyes. You can fix the problem with special moisturizing drops.
In the early days of using lenses, a person may notice colored reflections and light circles around light sources. Their appearance is caused by an active change in the shape of the cornea. Soon, all unpleasant symptoms disappear, the patient gets used to the lenses and feels great. After 1-2 weeks, his vision rises to 100%.
Currently, orthokeratology can correct many visual defects. Best Results available for myopia up to -00; Hypermetropia up to 00; Cylinder to -00; presbyopia before. Only after a visit to a specialist and after some preliminary tests will your trust center confirm that you are a suitable subject for the use of orthokeratological lenses.
How Orthokeratology Works
Orthokeratology is a non-surgical and non-invasive technique for the reversible reduction of myopia, astigmatism, hypermetropia and presbyopia through special contact lenses called "reverse geometry". These are rigid translucent gas lenses designed to simulate the effect of a corneal profile and remain well centered on the eye even when the eyelid is closed.
Can there be complications?
Night lenses for vision correction cause complications much less often than usual. Since they are made of breathable materials, they do not interfere with the breathing of the cornea. Moreover, they are very convenient to use and do not violate the habitual way of life of a person. Unwanted Consequences appear in case misuse lenses.
The lenses used for orthokeratology are highly complex lenses that allow oxygen to reach the eye even when the eyelid is closed. When wearing the lens, you will be clearly visible as if you were wearing a normal corrective lens. When you remove it, you will continue to see well even with the naked eye.

Myopia in sports, in any sport, whether outdoors or in other environments, can pose a real problem. Orthokeratology addresses this issue by avoiding the use of glasses and normal contact lenses for many athletes, allowing them the freedom to pursue their favorite activities. With orthokeratology, those involved in sports see an increase in safety and, above all, the possibility of breaking glasses or losing contact lenses during sports activities disappears. Today it is possible to freely enjoy the opportunity to play sports in complete freedom, without using contact lenses or glasses.
Possible complications:
- under-correction or over-correction;
- swelling, inflammation, erosion of the cornea;
- allergic conjunctivitis and keratitis.
With careful care of the lenses, you can avoid any unpleasant complications. In case of itching, discomfort, watery eyes or other suspicious symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor.
During work, and especially for certain types of work, the use of glasses or contact lenses during the day can be particularly difficult or uncomfortable. For those who work outdoors, they can increase the risk of abrasions caused by foreign bodies under the lenses or due to soft lens breakage and, above all, for myopia who must wear contact lenses, the use of protection is not always enough. Just like glasses that are constantly covered in dust can create serious problems for those who work on the construction site.
night lens care
Lenses to restore vision should be worn at night and removed in the morning. After removing them, gently wipe them with your fingertips and rinse with running water. Store lenses in a special container with. The liquid must be changed every day, and the container - at least once every 3 months. The lens remover is recommended to be used no longer than 6 months.
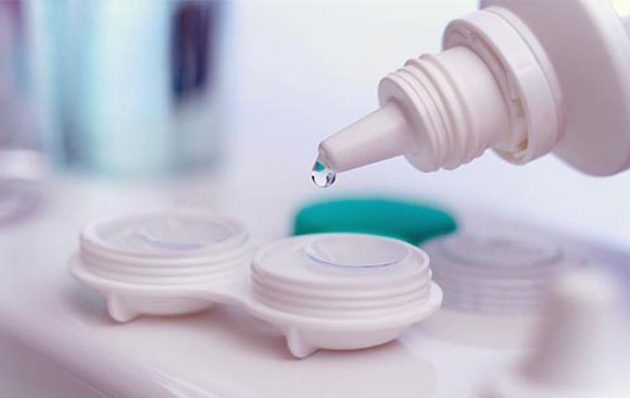
Rigid lenses should be used carefully and carefully. They are made of a hard but brittle material, so they can easily break if dropped or crushed. If chips, scratches, cracks or other major defects appear in the lenses, they will have to be replaced with new ones.
Orthokeratology enables people to see clearly without glasses or vision correction surgery. To do this, they just need to put on special hard lenses at night. In the morning, after removing them, vision is restored to 100% and remains so all day. Orthokeratology lenses are comfortable and safe to use, which is why they are increasingly being used for vision correction.
Useful video about night lenses
The effect of night lenses is reversible, which makes it necessary to wear orthokeratological lenses every night or every other night (this parameter is individual).
The first orthokeratological (OK) lenses, and with them the term itself, appeared in the early 60s. True, at that time it was necessary to wear lenses enough a long period, and the results of OK therapy were difficult to predict, so this method not received wide distribution. In the early 90s, with the advent of modern diagnostic equipment and the possibility of manufacturing contact lenses of complex geometry, orthokeratology received a new impetus to development.
In the early 2000s, for the first time, they started talking about night OK therapy: putting on lenses at night, the patient removes them in the morning, and the next day he sees perfectly without any corrective optics.
Correction range
According to numerous studies, it is reported that 100% correction with night OK lenses is possible in the range from -1.5 to -4 diopters (D). However, there are reports of possible correction myopia and -5 D. Moreover, some patients managed to correct myopia -6 D.
The greatest effect of correction (up to 75%) of vision, as a rule, is achieved already in the first use of such lenses. Full correction and stabilization of the results occurs by 7-10 days of using night lenses. During the day, when the lenses are not worn, there is a slight decrease in the effect, down to -0.75 diopters. Maintaining long-term vision correction requires the use of OK lenses every night or every 2 or 3 nights. Usually patients are satisfied with the mode of wearing lenses night after night.
OK lenses have no age restrictions, they are suitable for children and adolescents, which is very important, because up to 18 years surgery myopia cannot be carried out. Such lenses are also suitable for adults who, for some reason, contact correction is impossible or there are contraindications to surgery.
How it works?
With myopia, light rays, passing through the optical media of the eyes, have the property before. In order for the focus to fall on , it is necessary to "weaken" the refraction of the rays. This is achieved by changing the shape, for which it is necessary to make it flatter. By the way, it is this principle that underlies most surgical techniques vision correction. Orthokeratology also uses it: rigid lenses, by pressing down on the cornea, make it flatter, as they provoke a redistribution surface layers cells, which, in turn, refract light rays more weakly, and the image is focused on the retina. After removing night lenses, the cornea can retain its shape for some time, and the patient sees well without any correction. But gradually the cornea is leveled to its original shape, and OK lenses have to be put on again.
Benefits of ok therapy
Night OK therapy has a number of important advantages in relation to other methods of vision correction:
First and foremost, during the day the patient does not need correction at all, i.e. it is free from glasses, lenses and any restrictions that come with poor eyesight. It is worth recalling that in some cases, spectacle or contact correction is simply unacceptable due to the type of activity of the patient (pilots, swimmers, hockey players, etc.), and surgical treatment is delayed due to medical indications or personal reluctance. In such cases, the only possible option are night lenses.
In these lenses, the cornea of the eye does not suffer from a chronic lack of oxygen, as when wearing contact lenses all the time, because during the day the patient is without them, and oxygen has free access to the cornea. At the same time, we will not deny that at night, in the presence of lenses and closed ones, hypoxia intensifies. But during the day, nighttime hypoxia is more than compensated by free access to the cornea of air and oxygen. Also excellent eyesight.
Wearing contact lenses significantly reduces the frequency of blinking movements and impairs tear flow, which becomes the cause. OK therapy minimizes the risk of dry eye syndrome, as the lenses are daytime missing, and physiological mechanism distribution of tear fluid is preserved. Together with the tear, nutrients and bactericidal substances enter, are removed tiny particles dust, microorganisms, metabolic products.
The use of OK lenses practically does not give impetus to the development allergic manifestations, in addition, the risk of occurrence of and decreases.
With such lenses, you can use any cosmetics and not be afraid that its particles will settle on the surface of contact lenses.
No need to remove lenses when swimming, or swim with protective glasses. In OK lenses, high-speed driving by car or bicycle is possible without fear that the lenses will “dry” in the wind.
There is no need for a container for lenses, as well as the need to apply drops after talking with smoking friends in a confined space.
If in time the opportunity surgical correction becomes achievable, then you should just stop wearing OK lenses. After some time, the cornea will return to its original shape and the operation will take place.
How to choose OK lenses and possible complications
Orthokeratology lenses should only be fitted by a specialist in OK therapy. During the examination, the doctor performs certain diagnostic procedures:
(measurement of the curvature of the cornea);
(drawing up a "map" of the surface of the cornea);
Finds out all the contraindications for the use of such lenses.
Only after that, the procedure for selecting night lenses begins. Sometimes more than one pair of OK lenses is moved before the desired effect is achieved, and the lenses are prescribed for regular wear at night.
The final improvement in vision after the first application does not occur. It takes about two weeks to become less by 2-3 diopters.
At first, the patient may be disturbed various disorders vision: glare from light sources, blurred and light images. Often such side effects long time do not go away, then you have to either select other OK lenses, or completely abandon OK therapy.
This type of contact lenses is designed for a year of operation, they must be stored in a disinfectant solution. About once every six months, you should visit an ophthalmologist for preventive purposes.
The use of OK lenses can cause complications that are typical for any type of contact correction: erosion, hyper- or hypocorrection, complications infectious nature. In the event of any unpleasant symptoms you need to contact a specialist immediately.
Microtrauma while wearing contact lenses
When wearing contact lenses, the cornea experiences daily stress, microtraumas appear on its surface, accompanied by pain symptoms, feeling foreign body in the eye, lacrimation and redness of the conjunctiva. To restore the tissues of the ocular surface, after injuries, as adjuvant therapy, products with dexpanthenol can be used - a substance that has a regenerating effect on tissues, in particular, eye gel Korneregel. It has a healing effect due to the maximum concentration of dexpanthenol 5% *, and the carbomer included in its composition prolongs the contact of dexpanthenol with the ocular surface due to its viscous texture. Korneregel remains on the eye for a long time due to its gel-like form, is easy to apply, penetrates into the deep layers of the cornea and stimulates the process of regeneration of the epithelium of the surface tissues of the eye, promotes the healing of microtraumas and eliminates the sensation of pain. The drug is applied in the evening, when the lenses are already removed.
The cost of oc-therapy
The OK-therapy procedure is a rather costly event, the cost of which in some cases can be half the cost of the vision procedure. This is easily explained, because its price includes the cost special studies, the time spent by a specialist on the selection of OK lenses, multiple visits to the doctor during the initial period of adaptation, which are necessary to obtain the best effect.
However, all these costs pay off, because OK lenses are designed for a very long period of use, and you do not often have to spend money on buying a new pair of lenses. In addition, sometimes good spectacle frame and high-quality lenses are also more expensive than surgical vision correction. And most importantly, you need to understand that orthokeratology is modern method correction of myopia, which allows you to do what you love, which would be impossible with spectacle or contact correction.
