Formula for pressure of air, steam, liquid or solid. How to find pressure (formula)? See what “Pressure (physics)” is in other dictionaries
Pressure is a physical quantity that plays a special role in nature and human life. This invisible phenomenon not only affects the condition environment, but also very well felt by everyone. Let's figure out what it is, what types it exists and how to find pressure (formula) in different environments.
What is pressure in physics and chemistry?
This term refers to an important thermodynamic quantity, which is expressed in the ratio of the pressure force exerted perpendicularly to the surface area on which it acts. This phenomenon does not depend on the size of the system in which it operates, and therefore refers to intensive quantities.
In a state of equilibrium, the pressure is the same for all points of the system.
In physics and chemistry it is denoted by the letter “P”, which is an abbreviation for Latin name term - pressūra.
If we're talking about about the osmotic pressure of a liquid (the balance between the pressure inside and outside the cell), the letter “P” is used.
Pressure units
According to the standards of the International SI System, the physical phenomenon in question is measured in pascals (Cyrillic - Pa, Latin - Ra).
Based on the pressure formula, it turns out that one Pa is equal to one N (newton - divided by one square meter (unit of area).
However, in practice it is quite difficult to use pascals, since this unit is very small. In this regard, in addition to SI standards, this quantity can be measured differently.
Below are its most famous analogues. Most of them are widely used in the former USSR.
- Bars. One bar is equal to 105 Pa.
- Torrs, or millimeters of mercury. Approximately one torr corresponds to 133.3223684 Pa.
- Millimeters of water column.
- Meters of water column.
- Technical atmospheres.
- Physical atmospheres. One atm is equal to 101,325 Pa and 1.033233 atm.
- Kilogram-force per square centimeter. Ton-force and gram-force are also distinguished. In addition, there is an analogue to pound-force per square inch.
General formula for pressure (7th grade physics)
From the definition of a given physical quantity, one can determine the method for finding it. It looks like in the photo below.

In it, F is force and S is area. In other words, the formula for finding pressure is its force divided by the surface area on which it acts.
It can also be written as follows: P = mg / S or P = pVg / S. Thus, this physical quantity turns out to be related to other thermodynamic variables: volume and mass.
Valid for pressure next principle: the smaller the space that is affected by the force, the greater the amount of pressing force that falls on it. If the area increases (with the same force), the desired value decreases.
Hydrostatic Pressure Formula
Different states of aggregation substances, provide for the presence of different properties from each other. Based on this, the methods for determining P in them will also be different.
For example, the formula for water pressure (hydrostatic) looks like this: P = pgh. It also applies to gases. However, it cannot be used to calculate atmospheric pressure due to the difference in altitude and air density.
In this formula, p is the density, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and h is the height. Based on this, the deeper an object or object is immersed, the higher the pressure exerted on it inside the liquid (gas).

The option under consideration is an adaptation of the classic example P = F / S.
If we remember that the force is equal to the derivative of mass by the speed of free fall (F = mg), and the mass of the liquid is the derivative of volume by density (m = pV), then the formula pressure can be written as P = pVg / S. In this case, volume is area multiplied by height (V = Sh).
If we insert this data, it turns out that the area in the numerator and denominator can be reduced at the output - the above formula: P = pgh.
When considering pressure in liquids, it is worth remembering that, unlike solids, curvature of the surface layer is often possible in them. And this, in turn, contributes to the formation of additional pressure.
For such situations, a slightly different pressure formula is used: P = P 0 + 2QH. In this case, P 0 is the pressure of the non-curved layer, and Q is the tension surface of the liquid. H is the average curvature of the surface, which is determined according to Laplace's Law: H = ½ (1/R 1 + 1/R 2). The components R 1 and R 2 are the radii of the main curvature.
Partial pressure and its formula
Although the P = pgh method is applicable for both liquids and gases, it is better to calculate the pressure in the latter in a slightly different way.
The fact is that in nature, as a rule, absolutely pure substances are not very often found, because mixtures predominate in it. And this applies not only to liquids, but also to gases. And as you know, each of these components exerts a different pressure, called partial.
It's quite easy to define. It is equal to the sum of the pressure of each component of the mixture under consideration (ideal gas).
It follows from this that the partial pressure formula looks like this: P = P 1 + P 2 + P 3 ... and so on, according to the number of constituent components.

There are often cases when it is necessary to determine air pressure. However, some people mistakenly carry out calculations only with oxygen according to the scheme P = pgh. But air is a mixture of different gases. It contains nitrogen, argon, oxygen and other substances. Based on the current situation, the air pressure formula is the sum of the pressures of all its components. This means that we should take the above-mentioned P = P 1 + P 2 + P 3 ...
The most common instruments for measuring pressure
Despite the fact that it is not difficult to calculate the thermodynamic quantity in question using the above-mentioned formulas, sometimes there is simply no time to carry out the calculation. After all, you must always take into account numerous nuances. Therefore, for convenience, over several centuries a number of devices have been developed that do this instead of people.
In fact, almost all devices of this kind are a type of pressure gauge (helps determine pressure in gases and liquids). However, they differ in design, accuracy and scope of application.
- Atmospheric pressure is measured using a pressure gauge called a barometer. If it is necessary to determine the vacuum (that is, pressure below atmospheric), another type of it is used, a vacuum gauge.
- In order to find out arterial pressure in humans, a sphygmomanometer is used. It is better known to most people as a non-invasive blood pressure monitor. There are many varieties of such devices: from mercury mechanical to fully automatic digital. Their accuracy depends on the materials from which they are made and the location of measurement.
- Pressure drops in the environment (in English - pressure drop) are determined using differential pressure meters (not to be confused with dynamometers).
Types of pressure
Considering pressure, the formula for finding it and its variations for different substances, it is worth learning about the varieties of this quantity. There are five of them.
- Absolute.
- Barometric
- Excessive.
- Vacuum metric.
- Differential.
Absolute
This is the name of the total pressure under which a substance or object is located, without taking into account the influence of other gaseous components of the atmosphere.
It is measured in pascals and is the sum of excess and atmospheric pressure. It is also the difference between barometric and vacuum types.
It is calculated using the formula P = P 2 + P 3 or P = P 2 - P 4.
The starting point for absolute pressure under the conditions of planet Earth is the pressure inside the container from which air has been removed (that is, a classic vacuum).
Only this type of pressure is used in most thermodynamic formulas.
Barometric
This term refers to the pressure of the atmosphere (gravity) on all objects and objects found in it, including the surface of the Earth itself. Most people also know it as atmospheric.
It is classified as one and its value varies relative to the place and time of measurement, as well as weather conditions and location above/below sea level.
The magnitude of barometric pressure is equal to the modulus of the atmospheric force over an area of one unit normal to it.
In a stable atmosphere, the magnitude of this physical phenomenon is equal to the weight of a column of air on a base with an area equal to one.
The normal barometric pressure is 101,325 Pa (760 mm Hg at 0 degrees Celsius). Moreover, the higher the object is from the surface of the Earth, the lower the air pressure on it becomes. Every 8 km it decreases by 100 Pa.

Thanks to this property, water in kettles boils much faster in the mountains than on the stove at home. The fact is that pressure affects the boiling point: as it decreases, the latter decreases. And vice versa. The operation of such kitchen appliances as a pressure cooker and autoclave is based on this property. An increase in pressure inside them contributes to the formation of more high temperatures than in regular pans on the stove.

The barometric altitude formula is used to calculate atmospheric pressure. It looks like in the photo below.

P is the desired value at altitude, P 0 is the air density near the surface, g is the free fall acceleration, h is the height above the Earth, m is the molar mass of the gas, t is the temperature of the system, r is the universal gas constant 8.3144598 J⁄( mol x K), and e is the Eichler number equal to 2.71828.
Often in the above formula for atmospheric pressure, K - Boltzmann's constant is used instead of R. The universal gas constant is often expressed through its product by Avogadro's number. It is more convenient for calculations when the number of particles is given in moles.
When making calculations, you should always take into account the possibility of changes in air temperature due to a change in meteorological situation or when gaining altitude above sea level, as well as geographic latitude.

Gauge and vacuum
The difference between atmospheric and measured ambient pressure is called excess pressure. Depending on the result, the name of the quantity changes.
If it is positive, it is called gauge pressure.
If the result obtained has a minus sign, it is called vacuummetric. It is worth remembering that it cannot be greater than barometric.
Differential
This value is the pressure difference in various points measurements. As a rule, it is used to determine the pressure drop on any equipment. This is especially true in the oil industry.
Having figured out what kind of thermodynamic quantity is called pressure and with what formulas it is found, we can conclude that this phenomenon is very important, and therefore knowledge about it will never be superfluous.
If general health deteriorates, it is necessary to measure an indicator such as blood pressure (hereinafter referred to as blood pressure), since in this way hypotension or hypertension can be determined. In the first case blood pressure pathologically decreases, and in the second increases. Before we talk about progressive pathological process, it is important to understand in detail what is normal pressure person, and what it should be.
What is blood pressure
This is the force that blood exerts on the walls of blood vessels during systemic circulation. Such important parameter the viability of the body is characterized by the total peripheral vascular resistance, in the case of fatal outcome tends to zero. The process of compression of the walls of capillaries, arteries and veins under the influence of systemic blood flow is a complex mechanism subject to the pathogenic influence of provoking factors. This indicator will depend on healthy body, or take place dangerous diseases. The norm varies by age and gender.
Types of pressure
Many patients have noticed that blood pressure, after being measured with a tonometer, is written in the form of a fraction, where the first and second numbers are radically different in value. To understand what these numbers are, it’s time to remember the conditional classification of such an important indicator of the functionality of the systemic blood flow. Doctors distinguish upper and lower, each of which has its own characteristics:
- Upper blood pressure (systolic). Determined at the moment of contraction of the heart muscle. The resulting indicator depends on heart rate, tone blood vessels, myocardial contraction forces. Normal indicator is in the range of 110-120 mm. rt. Art. Its abnormal deviation is influenced not only by the pathologies present in the body, but also physical exercise, age-related changes body.
- Lower blood pressure (diastolic). It is determined at the moment of relaxation of the heart muscle. The real indicator depends on arterial tone, total blood volume, and the elasticity of the vascular walls. Within normal limits, the lower arterial varies between 70-80 mm. rt. Art. If a dangerous pathology occurs, the specified value is outside the permissible limits.
Normal by age
In adulthood, indicators differ not only by year, but also by the gender of the patient. Every person simply must know what acceptable blood pressure levels exist in their case, so that after measuring with the device, they can reduce the likelihood of relapses dangerous pathologies more often from the cardiac system. Below is a table indicating what ideally blood pressure should be in adult women and men, according to age category.
| Patient age | ||
| 110 – 120/70 – 75 | 120 – 125/70 – 80 |
|
| 115 – 120/70 – 80 | 120 – 127/75 – 80 |
|
| 120 – 130/80 – 85 | 125 – 130/80 – 85 |
|
| 135 – 140/80 – 85 | 130 – 135/80 – 85 |
|
| 140 – 145/85 – 90 | 135 – 145/85 – 90 |
|
| 145 – 155/85 – 90 | 135 – 145/80 – 85 |
During pregnancy, there is a high probability of mild hypertension, which is an acceptable normal limit. This deviation is explained by a doubling of systemic blood flow due to the presence of new life in the womb. Getting rid of such a disorder is a matter of time, so there is no need to take medications with synthetic substances in vain. active ingredients– they won’t help the pregnant woman, and they can harm the baby.
How to find out your numbers
To determine the blood pressure in your own body, you need to use a special medical device called a tonometer. It can be used in home environment, and with proper handling, with high accuracy it states the fact of an increase and decrease in permissible blood pressure limits. Characteristic vibrations can be determined in two ways: physiological means:
- Korotkov method. This is the most common diagnostic method, developed by the surgeon Korotkov back in 1905. For measurements, a classic tonometer is used, which structurally consists of a cuff with a bulb, a phonendoscope, and a pressure gauge.
- Oscillometric method. In this case, modern electronic devices are used, which are necessary to record pulse fluctuations as blood passes through the section of the vessel compressed by the cuff.

Increased
Before you cure vascular disease, it is required to determine with utmost accuracy the main causes of increased blood pressure, to promptly eliminate the provoking factor and its unpleasant symptoms. We are talking about pathology if, after a characteristic measurement, the tonometer shows a limit of more than 140/90 mm Hg. Art. Doctors distinguish 2 types arterial hypertension:
- primary (essential) hypertension, which can be determined after careful clinical examination;
- secondary hypertension, which is an unpleasant symptom of the underlying disease of the body.
Symptoms
If we are talking about arterial hypertension, the first sign of a characteristic disease is a jump in blood pressure above the permissible limit. The disease may prevail for some time hidden form, but in case of systematic relapses, you should not engage in dangerous self-medication; it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and undergo full examination. It is necessary to pay attention not only to high blood pressure, but also to following symptoms arterial hypotension:
- tinnitus;
- noise in the head;
- migraine attacks with throbbing at the temple;
- spots before the eyes, loss of vision sharpness;
- frequent dizziness;
- symptoms of cerebral hypoxia;
- frequent urination;
- nausea, less often – vomiting;
- hypertensive crisis, heart pain;
- a sharp decline in performance.
Causes
If arterial pressure has increased pathologically, the culprit is often extensive pathologies of the thyroid gland, kidneys, adrenal glands, hormonal imbalance. The body experiences increased production natural hormone called renin, resulting in increased tone blood vessels, the myocardium contracts too often, the pulse increases abnormally. The reasons for such extensive pathology may be as follows:
- diabetes;
- one of the forms of obesity;
- passive lifestyle;
- presence of bad habits;
- chronic stress;
- poor nutrition;
- chronic diseases myocardium.
Low
In this case we are talking about arterial hypotension, which can be independent or secondary disease, requires immediate conservative treatment. When measuring blood pressure, the device shows a deviation in which the blood pressure indicates an interval of less than 90/60 mmHg. Art. This condition can be physiological and temporary (it is not considered pathological), but if blood pressure regularly deviates downward, doctors suspect hypotension.
Symptoms
Such a diagnosis also poses a significant health hazard, therefore, if hypotension is suspected, the patient is required to perform a characteristic measurement with a tonometer several times a day at home. Other signs of this pathology are presented in detail below, and should not be ignored by the potential patient:
- nausea and dizziness;
- absentmindedness;
- decreased memory functions;
- dyspnea;
- migraine attacks;
- increased fatigue;
- decline in performance.

Causes
Before using any medications and starting treatment yourself, it is necessary to promptly identify the pathogenic factor of arterial hypotension and eliminate it. The attending physician recommends full diagnostics body, an important component of which is the collection of anamnesis data. The causes of a characteristic illness may be as follows:
- any type of anemia;
- severe blood loss;
- complete or partial dehydration of the body;
- chronic myocardial diseases;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- medication overdose;
- hypothyroidism
How to treat blood pressure
Knowing the principle of development of such cardiac pathology, it is important to correctly and timely select intensive care which is allowed to be carried out at home. Taking medications depends on the level of blood pressure, chronic diseases of the body, and the age of the patient. Regulation of blood in the vessels is achieved by medication, however, the patient will additionally have to reconsider his usual lifestyle and give up bad habits forever. List effective medicines detailed below.
Increased
A systematically elevated blood pressure level means that the patient is a chronic hypertensive patient and is under systematic monitoring by a cardiologist. In such clinical picture course admission of representatives of the following is required pharmacological groups to prolong the period of remission of the underlying disease, reduce blood pressure and get rid of unpleasant symptoms:
- ACE inhibitors that dilate vascular walls: Fosinopril, Captopril, Ramipril, Enalapril, Lisinopril, Perindopril;
- beta blockers that reduce the minute volume of systemic blood flow: Bisoprolol, Atenolol, Nebivolol, Metoprolol;
- diuretics to reduce portions of fluid in the systemic circulation: Furosemide, Chlorthalidone, Torasemide, Indapamide;
- sartans, also known as angiotensin receptor blockers: Losartan, Valsartan, Losartan, Valsartan, Telmisartan;
- calcium channel blockers that expand the lumen in peripheral vessels: Amlodipine, Verapamil, Nifedipine, Diltiazem.
Decreased
If there are obvious signs of hypotension, it is recommended to consume caffeine and vitamin C, while completely eliminating bad habits, lead active image life, eat more sweets. Among medications, the medical drug Etimizol is particularly effective. However, doctors also prescribe biological phytostimulants, represented by infusion Chinese lemongrass or aralia, extracts of eleutherococcus, ginseng, echinacea, radiola. If arterial pressure has pathologically decreased, the natural drug Pantocrine is recommended to reduce the risk of collapse.
Treatment of blood pressure with folk remedies
In order to achieve normal blood pressure by age, you can use alternative medicine methods, but first obtain medical support and do not self-medicate. To regulate blood pressure levels, the patient is recommended to use following recipes traditional treatment, characterized high efficiency:
- For hypertension, you need to fill a full liter jar with open buds, pour vodka to the neck, cover with a lid and leave in a dark place. Use the prepared tincture orally after straining 1 tsp. three times a day before each meal.
- For hypotension, you should combine 20 g of hawthorn berries, ginseng root, chamomile and astragalus flowers in one container. Pour a tablespoon of raw material into a glass of boiling water, leave, strain. Take a third of a glass orally three times a day until blood pressure rises.

Prevention
To ensure that your blood pressure does not deviate from the norm, you must completely eliminate bad habits, control your coffee consumption, eat right, take multivitamin complexes. In addition, others preventive actions are presented below:
- visit more often fresh air;
- increase physical activity;
- exercise;
- promptly treat heart and vascular diseases;
- monitor your general health.
Video
Everything is quite simple. It is one of the main indicators of activity of cardio-vascular system. Let's look at this issue in more detail.
What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the process of compression of the walls of capillaries, arteries and veins under the influence of blood circulation.
Types of blood pressure:
- upper, or systolic;
- lower, or diastolic.
Both of these values should be taken into account when determining your blood pressure level. The very first units of its measurement remain - millimeters of mercury. This is because older machines used mercury to determine blood pressure levels. Therefore, the blood pressure indicator looks like this: upper blood pressure (for example, 130) / lower blood pressure (for example, 70) mm Hg. Art.
Circumstances that directly affect blood pressure range include:
- the level of force of contractions performed by the heart;
- the proportion of blood ejected by the heart during each contraction;
- resistance of the walls of blood vessels, which is the flow of blood;
- the amount of blood circulating in the body;
- pressure fluctuations in chest which are caused by the respiratory process.
Blood pressure levels can change throughout the day and as you age. But for most healthy people characterized by a stable blood pressure.
Determination of types of blood pressure
Systolic (upper) blood pressure is a characteristic general condition veins, capillaries, arteries, as well as their tone, which is caused by contraction of the heart muscle. It is responsible for the work of the heart, namely with what force the latter is able to push out blood.
Thus, the level of upper pressure depends on the strength and speed with which heart contractions occur.
It is unreasonable to assert that arterial and cardiac pressure are the same concept, since the aorta also participates in its formation.

The lower one characterizes the activity of blood vessels. In other words, this is the blood pressure level at the moment when the heart is most relaxed.
Lower pressure is formed as a result of contraction of the peripheral arteries, through which blood enters the organs and tissues of the body. Therefore, the state of blood vessels - their tone and elasticity - is responsible for the level of blood pressure.
How to find out your blood pressure level?
You can find out your blood pressure level using a special device called a “blood pressure tonometer”. This can be done either at the doctor (or nurse) or at home, after purchasing the device at the pharmacy.
The following types of tonometers are distinguished:
- automatic;
- semi-automatic;
- mechanical.

A mechanical tonometer consists of a cuff, a pressure gauge or display, an inflation bulb, and a stethoscope. How it works: put the cuff on your arm, place a stethoscope under it (you should hear your pulse), inflate the cuff with air until it stops, and then begin to gradually deflate it by unscrewing the wheel on the bulb. At some point, you will clearly hear pulsating sounds in the headphones of the stethoscope, then they will stop. These two marks are the upper and lower blood pressure.
Consists of a cuff, electronic display and bulb. How it works: put on a cuff, inflate the bulb to the maximum, then release it. The electronic display shows the upper and lower values of blood pressure and the number of beats per minute - pulse.
An automatic blood pressure monitor consists of a cuff, an electronic display and a compressor, which performs manipulations to pump and deflate air. How it works: put on the cuff, start the device and wait for the result.
It is generally accepted that a mechanical tonometer gives the most exact result. It is also more affordable. At the same time, automatic and semi-automatic blood pressure monitors remain the most convenient to use. Such models are especially suitable for older people. Moreover, some types have a voice notification function for pressure indicators.
You should measure blood pressure no earlier than thirty minutes after any physical activity (even minor) and an hour after drinking coffee and alcohol. Before the measurement process itself, you need to sit quietly for a couple of minutes and catch your breath.
Blood pressure - normal by age
Each person has an individual one that may not be associated with any diseases.
Blood pressure levels are determined by a number of factors that are of particular importance:
- age and gender of the person;
- personal characteristics;
- life style;
- lifestyle features, preferred type of recreation, and so on).

Blood pressure also tends to increase when performing unusual physical activity and emotional stress. And if a person constantly performs physical activity (for example, an athlete), then the blood pressure level may also change both for time and for a long period. For example, when a person is under stress, then his blood pressure can rise to thirty mm Hg. Art. from the norm.
However, there are still certain limits for normal blood pressure. And every ten points of deviation from the norm indicates a disruption in the functioning of the body.
Age | Upper level of blood pressure, mm Hg. Art. | Lower blood pressure level, mm Hg. Art. |
1 - 10 years | ||
from 95 to 110 | ||
16 - 20 years | from 110 to 120 | |
21 - 40 years | from 120 to 130 | |
41 - 60 years | ||
61 - 70 years | from 140 to 147 | |
Over 71 years old |
You can also calculate your individual blood pressure using the following formulas:
1. For men:
- upper blood pressure = 109 + (0.5 * number full years) + (0.1 * weight in kg);
- lower blood pressure = 74 + (0.1 * number of completed years) + (0.15 * weight in kg).
2. For women:
- upper blood pressure = 102 + (0.7 * number of completed years) + 0.15 * weight in kg);
- lower blood pressure = 74 + (0.2 * number of completed years) + (0.1 * weight in kg).
Round the resulting value to a whole number according to the rules of arithmetic. That is, if the result is 120.5, then when rounded it will be 121.
Increased blood pressure
High blood pressure is high level at least one of the indicators (lower or upper). The degree of its overestimation should be judged by taking into account both indicators.
Regardless of whether lower blood pressure is high or high, it is a disease. And it's called hypertension.

There are three degrees of the disease:
- first - SBP 140-160 / DBP 90-100;
- second - SBP 161-180 / DBP 101-110;
- third - SBP 181 and more / DBP 111 and more.
It is worth talking about hypertension when there is a high level of blood pressure values over a long period.
According to statistics, this figure is overestimated systolic pressure is most often observed in women, and diastolic - in men and the elderly.
Symptoms of high blood pressure may include:
- decreased performance;
- the appearance of fatigue;
- frequent feeling of weakness;
- morning pain in the back of the head;
- frequent dizziness;
- the appearance of nosebleeds;
- noise in ears;
- decreased visual acuity;
- appearing at the end of the day.
Causes of high blood pressure
If it is lower arterial, then most likely this is one of the symptoms of a disease of the thyroid gland, kidneys, adrenal glands, which have begun to produce renin in large quantities. It, in turn, increases the tone of the muscles of blood vessels.
Increased lower blood pressure is fraught with the development of further more serious diseases.
High upper pressure indicates too frequent heart contractions.
A jump in blood pressure can be caused by a number of reasons. This is for example:
- narrowing of blood vessels as a result of atherosclerosis;
- overweight;
- diabetes;
- stressful situations;
- poor nutrition;
- excessive consumption of alcohol, strong coffee and tea;
- smoking;
- lack of physical activity;
- frequent weather changes;
- some diseases.
What is low blood pressure?
Low blood pressure is vegetative-vascular dystonia or hypotension.
What happens with hypotension? When the heart contracts, blood enters the vessels. They expand and then gradually narrow. Thus, the vessels help the blood move further along the circulatory system. The pressure is normal. For a number of reasons, vascular tone may decrease. They will remain expanded. There is then not enough resistance for blood movement, which causes the pressure to drop.

Blood pressure level for hypotension: upper - 100 or less, lower - 60 or less.
If the pressure drops sharply, blood supply to the brain is limited. And this is fraught with consequences such as dizziness and fainting.
Symptoms may include:
- increased fatigue and lethargy;
- the appearance of darkening in the eyes;
- frequent shortness of breath;
- feeling of coldness in the hands and feet;
- increased sensitivity to loud sounds and bright light;
- muscle weakness;
- motion sickness in transport;
- frequent headaches.
What is the cause of low blood pressure?
Poor joint tone and low blood pressure (hypotension) may be present from birth. But more often the culprits low blood pressure become:
- Extreme fatigue and stress. Overwork at work and at home, stress and lack of sleep cause a decrease in vascular tone.
- It's hot and stuffy. When you sweat, your body leaves a large number of liquids. For the sake of maintaining water balance it pumps water out of the blood that flows through the veins and arteries. Its volume decreases, vascular tone decreases. The pressure drops.
- Taking medications. Heart medications, antibiotics, antispasmodics and painkillers can “lower” blood pressure.
- Emergence allergic reactions for anything with possible anaphylactic shock.
If you haven't had hypotension before, don't leave it unpleasant symptoms without attention. They can be dangerous “bells” of tuberculosis, stomach ulcers, complications after a concussion and other diseases. See a therapist.
What to do to normalize blood pressure?
These tips will help you feel all cheerful day if you are hypotensive.
- Don't rush to get out of bed. When you wake up, do a short warm-up while lying down. Move your arms and legs. Then sit down and stand up slowly. Perform actions without sudden movements. they can cause fainting.
- Accept cold and hot shower in the morning for 5 minutes. Alternate the water - one minute warm, one minute cool. This will help you cheer up and is good for blood vessels.
- A cup of coffee is good for you! But only a natural tart drink will raise your blood pressure. Drink no more than 1-2 cups a day. If you have heart problems, drink coffee instead green tea. It invigorates no worse than coffee, and does not harm the heart.
- Sign up for the pool. Go at least once a week. Swimming improves vascular tone.
- Buy ginseng tincture. This natural “energetic energy” gives tone to the body. Dissolve 20 drops of tincture in ¼ glass of water. Drink half an hour before meals.
- Eat sweets. As soon as you feel weak, eat ½ teaspoon of honey or a little dark chocolate. Sweets will drive away fatigue and drowsiness.
- Drink clean water. Every day, 2 liters of pure and non-carbonated. This will help keep your blood pressure at a normal level. If you have heart and kidney problems, drinking regime must be prescribed by a doctor.
- Get enough sleep. A rested body will work as it should. Sleep at least 7-8 hours a day.
- Get a massage. According to experts oriental medicine, there are special points on the body. By influencing them, you can improve your well-being. The pressure is controlled by the point between the nose and upper lip. Gently massage it with your finger for 2 minutes clockwise. Do this when you feel weak.
First aid for hypotension and hypertension
If you feel dizzy, severe weakness, tinnitus, call an ambulance. While the doctors are on their way, take action:
- Unbutton the collar of your clothing. The neck and chest should be free.
- Lie down. Lower your head. Place a small pillow under your feet.
- Smell the ammonia. If you don't have it, use table vinegar.
- Have some tea. Definitely strong and sweet.

If you feel a hypertensive crisis approaching, then you also need to call a doctor. In general, this disease should always be supported preventive treatment. As first aid measures, you can resort to the following actions:
- Organize foot bath With hot water, to which mustard has been previously added. An alternative may be to apply mustard compresses to the heart area, back of the head and calves.
- Lightly wrap your right and then your left arm and leg for half an hour on each side. When the tourniquet is applied, the pulse should be palpable.
- Have a drink from chokeberry. It could be wine, compote, juice. Or eat jam from this berry.
To reduce the risk of occurrence and development of hypotension and hypertension, you should adhere to the regimen healthy eating, prevent the appearance excess weight, exclude harmful foods from the list, move more.
Blood pressure should be measured from time to time. If you observe a trend of high or low blood pressure, it is recommended to consult a doctor to determine the causes and prescribe treatment. Prescribed therapy may include methods to normalize blood pressure, such as taking special medications and herbal infusions, dieting, doing a set of exercises, and so on.
PHYSICS. 1. Subject and structure of physics Physics is a science that studies the simplest and at the same time the most important. general properties and the laws of motion of the objects of the material world around us. As a result of this commonality, there are no natural phenomena that do not have physical properties. properties... Physical encyclopedia
The science that studies the simplest and at the same time the most general patterns natural phenomena, the properties and structure of matter and the laws of its motion. The concepts of physiology and its laws underlie all natural science. F. belongs to the exact sciences and studies quantities ... Physical encyclopedia
PHYSICS- PHYSICS, a science that studies together with chemistry general laws transformations of energy and matter. Both sciences are based on two basic laws of natural science: the law of conservation of mass (Lomonosov’s law, Lavoisier) and the law of conservation of energy (R. Mayer, Jaul... ... Great Medical Encyclopedia
Stellar physics is one of the branches of astrophysics that studies the physical side of stars (mass, density, ...). Contents 1 Dimensions, masses, density, luminosity of stars 1.1 Mass of stars ... Wikipedia
I. Subject and structure of physics Physics is a science that studies the simplest and at the same time the most general laws of natural phenomena, the properties and structure of matter and the laws of its motion. Therefore, the concepts of F. and other laws underlie everything... ...
In a broad sense, pressure greater than atmospheric pressure; in specific technical and scientific tasks, pressure exceeding the value characteristic of each task. The division of D. v., which is equally conventionally found in the literature. to high and... Big Soviet encyclopedia
- (from ancient Greek physis nature). The ancients called physics any study of the surrounding world and natural phenomena. This understanding of the term physics remained until the end of the 17th century. Later, a number of special disciplines appeared: chemistry, which studies the properties... ... Collier's Encyclopedia
Study of the influence exerted on matter by very high pressures, as well as the creation of methods for obtaining and measuring such pressures. History of the development of physics high pressures an amazing example of unusually rapid progress in science,... ... Collier's Encyclopedia
Solid state physics is a branch of condensed matter physics whose task is to describe physical properties solids from the point of view of their atomic structure. It developed intensively in the 20th century after the discovery of quantum mechanics.... ... Wikipedia
Contents 1 Preparation methods 1.1 Evaporation of liquids ... Wikipedia
Books
- Physics. 7th grade. Workbook with Unified State Exam test tasks. Vertical. Federal State Educational Standard, Khannanova Tatyana Andreevna, Khannanov Nail Kutdusovich. The benefit is integral part UMK A. V. Peryshkina Physics. 7-9 grades`, which is redesigned in accordance with the requirements of the new Federal State educational standard. IN…
- Physics. 7th grade. Didactic materials for the textbook by A. V. Peryshkin. Vertical. Federal State Educational Standard, Maron Abram Evseevich, Maron Evgeniy Abramovich. This manual includes training tasks, tests for self-control, independent work, test papers and examples of solving typical problems. In total, the proposed set of didactic…
Imagine a sealed cylinder filled with air, with a piston installed on top. If you start to press on the piston, the volume of air in the cylinder will begin to decrease, air molecules will begin to collide with each other and with the piston more and more intensely, and the pressure of compressed air on the piston will increase.
If the piston is now sharply released, the compressed air will sharply push it upward. This will happen because, with a constant area of the piston, the force acting on the piston from the compressed air will increase. The area of the piston remained unchanged, but the force exerted by the gas molecules increased, and the pressure increased accordingly.
Or another example. A man stands on the ground, stands with both feet. In this position, a person is comfortable and does not experience any discomfort. But what happens if this person decides to stand on one leg? He will bend one of his legs at the knee, and will now rest on the ground with only one foot. In this position, a person will feel a certain discomfort, because the pressure on the foot has increased, approximately 2 times. Why? Because the area through which gravity now presses a person to the ground has decreased by 2 times. Here is an example of what pressure is and how easily it can be detected in everyday life.

From a physics point of view, pressure is called physical quantity, numerically equal to the force acting perpendicular to the surface per unit area of the given surface. Therefore, to determine the pressure at a certain point on the surface, the normal component of the force applied to the surface is divided by the area of the small surface element on which this force acts. And in order to determine the average pressure over the entire area, the normal component of the force acting on the surface must be divided by full area of this surface.
Pressure is measured in pascals (Pa). This unit of measurement of pressure got its name in honor of the French mathematician, physicist and writer Blaise Pascal, the author of the fundamental law of hydrostatics - Pascal's Law, which states that the pressure exerted on a liquid or gas is transmitted to any point without changes in all directions. The pressure unit "pascal" was first introduced into circulation in France in 1961, according to the decree on units, three centuries after the death of the scientist.
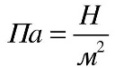
One pascal is equal to the pressure caused by a force of one newton, uniformly distributed, and directed perpendicular to a surface of one square meter.
Pascals measure not only mechanical pressure (mechanical stress), but also elastic modulus, Young's modulus, bulk modulus, yield strength, proportional limit, tensile strength, shear strength, sound pressure and osmotic pressure. Traditionally, it is in pascals that the most important mechanical characteristics of materials in strength materials are expressed.
Technical atmosphere (at), physical (atm), kilogram-force per square centimeter (kgf/cm2)
In addition to pascal, other (non-system) units are also used to measure pressure. One such unit is the “atmosphere” (at). The pressure of one atmosphere is approximately equal to the atmospheric pressure on the surface of the Earth at ocean level. Today, “atmosphere” refers to the technical atmosphere (at).

Technical atmosphere (at) is the pressure produced by one kilogram-force (kgf) distributed evenly over an area of one square centimeter. And one kilogram-force, in turn, is equal to the force of gravity acting on a body weighing one kilogram under conditions of gravitational acceleration equal to 9.80665 m/s2. One kilogram-force is thus equal to 9.80665 newton, and 1 atmosphere turns out to be equal to exactly 98066.5 Pa. 1 at = 98066.5 Pa.
For example, the pressure in car tires is measured in atmospheres; for example, the recommended tire pressure for the GAZ-2217 passenger bus is 3 atmospheres.
There is also a “physical atmosphere” (atm), defined as the pressure of a column of mercury, 760 mm high, at its base, given that the density of mercury is 13595.04 kg/m3, at a temperature of 0 ° C and under conditions of gravity acceleration equal to 9, 80665 m/s2. So it turns out that 1 atm = 1.033233 atm = 101,325 Pa.
As for kilogram-force per square centimeter (kgf/cm2), this extra-systemic unit of pressure is equal to normal atmospheric pressure with good accuracy, which is sometimes convenient for assessing various effects.
The off-system unit "bar" is approximately equal to one atmosphere, but is more accurate - exactly 100,000 Pa. In the CGS system, 1 bar is equal to 1,000,000 dynes/cm2. Previously, the name “bar” was given to a unit now called “barium” and equal to 0.1 Pa or in the CGS system 1 barium = 1 dyne/cm2. The words "bar", "barium" and "barometer" come from the same Greek word"heaviness".

The unit mbar (millibar), equal to 0.001 bar, is often used to measure atmospheric pressure in meteorology. And to measure pressure on planets where the atmosphere is very rarefied - μbar (microbar), equal to 0.000001 bar. On technical pressure gauges, most often the scale is graduated in bars.
Millimeter of mercury (mmHg), millimeter of water (mmHg)
The non-systemic unit of measurement “millimeter of mercury” is equal to 101325/760 = 133.3223684 Pa. It is designated “mmHg”, but is sometimes denoted “torr” - in honor of the Italian physicist, Galileo’s student, Evangelista Torricelli, the author of the concept of atmospheric pressure.
The unit was formed due to in a convenient way measuring atmospheric pressure with a barometer, in which the mercury column is in equilibrium under the influence of atmospheric pressure. Mercury has high density about 13600 kg/m3 and has low pressure saturated steam at room temperature, which is why mercury was chosen for barometers at one time.
At sea level, the atmospheric pressure is approximately 760 mm Hg, it is this value that is now considered normal atmospheric pressure, equal to 101325 Pa or one physical atmosphere, 1 atm. That is, 1 millimeter of mercury is equal to 101325/760 pascal.

Pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury in medicine, meteorology, and aviation navigation. In medicine, blood pressure is measured in mmHg, in vacuum technology it is graduated in mmHg, along with bars. Sometimes they even simply write 25 microns, meaning microns of mercury when we are talking about evacuation, and pressure measurements are carried out with vacuum gauges.
In some cases, millimeters of water column are used, and then 13.59 mm water column = 1 mm Hg. Sometimes this is more appropriate and convenient. A millimeter of water column, like a millimeter of mercury, is a non-systemic unit, equal in turn to the hydrostatic pressure of 1 mm of a water column, which this column exerts on a flat base at a water column temperature of 4 ° C.
